Sandbox: Difference between revisions
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
Readers might be amused trying to figure out what is going on. The claim seems to be that the pitch in question was | Readers might be amused trying to figure out what is going on. The terminology is unusual, but the main claim seems to be that the pitch in question was 1.8 standard deviations below the pitcher's average velocity. But surely Jeter's average is not independent of the type of pitch! | ||
==Accidental insights== | ==Accidental insights== | ||
Revision as of 20:47, 14 October 2014
Some math doodles
<math>P \left({A_1 \cup A_2}\right) = P\left({A_1}\right) + P\left({A_2}\right) -P \left({A_1 \cap A_2}\right)</math>
Derek Jeter
Peter Doyle forwarded the following story (originally from Bob Drake), which might be an extended Forsooth!
Derek Jeter Truther wants you to know the captain's final home game was rigged
by Dan Carson, Bleacher Report 26 September 2014
Baseball fans will know that Derek Jeter's Yankee Stadium career ended in storybook fashion with a game-winning hit in his final at bat. Skeptics were soon suggesting that the opposing pitcher had served up a soft pitch to facilitate these heroics. But one naysayer went so far as to conduct his own statistical analysis, which is reproduced in the article.
Readers might be amused trying to figure out what is going on. The terminology is unusual, but the main claim seems to be that the pitch in question was 1.8 standard deviations below the pitcher's average velocity. But surely Jeter's average is not independent of the type of pitch!
Accidental insights
My collective understanding of Power Laws would fit beneath the shallow end of the long tail. Curiosity, however, easily fills the fat end. I long have been intrigued by the concept and the surprisingly common appearance of power laws in varied natural, social and organizational dynamics. But, am I just seeing a statistical novelty or is there meaning and utility in Power Law relationships? Here’s a case in point.
While carrying a pair of 10 lb. hand weights one, by chance, slipped from my grasp and fell onto a piece of ceramic tile I had left on the carpeted floor. The fractured tile was inconsequential, meant for the trash.

As I stared, slightly annoyed, at the mess, a favorite maxim of the Greek philosopher, Epictetus, came to mind: “On the occasion of every accident that befalls you, turn to yourself and ask what power you have to put it to use.” Could this array of large and small polygons form a Power Law? With curiosity piqued, I collected all the fragments and measured the area of each piece.
| Piece | Sq. Inches | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 43.25 | 31.9% |
| 2 | 35.25 | 26.0% |
| 3 | 23.25 | 17.2% |
| 4 | 14.10 | 10.4% |
| 5 | 7.10 | 5.2% |
| 6 | 4.70 | 3.5% |
| 7 | 3.60 | 2.7% |
| 8 | 3.03 | 2.2% |
| 9 | 0.66 | 0.5% |
| 10 | 0.61 | 0.5% |
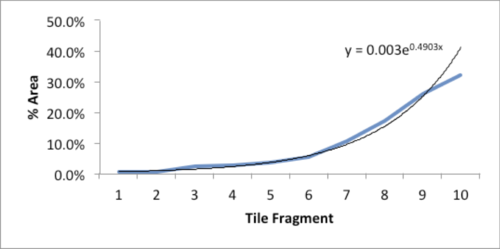
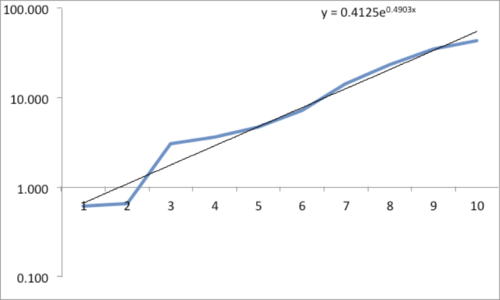
The data and plot look like a Power Law distribution. The first plot is an exponential fit of percent total area. The second plot is same data on a log normal format. Clue: Ok, data fits a straight line. I found myself again in the shallow end of the knowledge curve. Does the data reflect a Power Law or something else, and if it does what does it reflect? What insights can I gain from this accident? Favorite maxims of Epictetus and Pasteur echoed in my head: “On the occasion of every accident that befalls you, remember to turn to yourself and inquire what power you have to turn it to use” and “Chance favors only the prepared mind.”
My “prepared” mind searched for answers, leading me down varied learning paths. Tapping the power of networks, I dropped a note to Chance News editor Bill Peterson. His quick web search surfaced a story from Nature News on research by Hans Herrmann, et. al. Shattered eggs reveal secrets of explosions. As described there, researchers have found power-law relationships for the fragments produced by shattering a pane of glass or breaking a solid object, such as a stone. Seems there is a science underpinning how things break and explode; potentially useful in Forensic reconstructions. Bill also provided a link to a vignette from CRAN describing a maximum likelihood procedure for fitting a Power Law relationship. I am now learning my way through that.
Submitted by William Montante
